机器学习KNN-应用:手写数字识别(手撕+sklearn实现)_手写数字模型sklearn显示模型一百张数字-程序员宅基地
技术标签: 机器学习 python数据分析总结
参考链接
导入数据集
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 数据集的导入
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
load_digits()
{'data': array([[ 0., 0., 5., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 10., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 16., 9., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 6., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 2., ..., 12., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 10., ..., 12., 1., 0.]]),
'target': array([0, 1, 2, ..., 8, 9, 8]),
'frame': None,
'feature_names': ['pixel_0_0',
'pixel_0_1',
'pixel_0_2',
'pixel_0_3',
'pixel_0_4',
'pixel_0_5',
'pixel_0_6',
'pixel_0_7',
'pixel_1_0',
'pixel_1_1',
'pixel_1_2',
'pixel_1_3',
'pixel_1_4',
'pixel_1_5',
'pixel_1_6',
'pixel_1_7',
'pixel_2_0',
'pixel_2_1',
'pixel_2_2',
'pixel_2_3',
'pixel_2_4',
'pixel_2_5',
'pixel_2_6',
'pixel_2_7',
'pixel_3_0',
'pixel_3_1',
'pixel_3_2',
'pixel_3_3',
'pixel_3_4',
'pixel_3_5',
'pixel_3_6',
'pixel_3_7',
'pixel_4_0',
'pixel_4_1',
'pixel_4_2',
'pixel_4_3',
'pixel_4_4',
'pixel_4_5',
'pixel_4_6',
'pixel_4_7',
'pixel_5_0',
'pixel_5_1',
'pixel_5_2',
'pixel_5_3',
'pixel_5_4',
'pixel_5_5',
'pixel_5_6',
'pixel_5_7',
'pixel_6_0',
'pixel_6_1',
'pixel_6_2',
'pixel_6_3',
'pixel_6_4',
'pixel_6_5',
'pixel_6_6',
'pixel_6_7',
'pixel_7_0',
'pixel_7_1',
'pixel_7_2',
'pixel_7_3',
'pixel_7_4',
'pixel_7_5',
'pixel_7_6',
'pixel_7_7'],
'target_names': array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]),
'images': array([[[ 0., 0., 5., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 13., ..., 15., 5., 0.],
[ 0., 3., 15., ..., 11., 8., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 4., 11., ..., 12., 7., 0.],
[ 0., 2., 14., ..., 12., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 6., ..., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 5., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 9., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 3., ..., 6., 0., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 6., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 6., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 10., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 12., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 3., ..., 14., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 8., ..., 16., 0., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 9., 16., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 3., 13., ..., 11., 5., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 16., 9., 0.]],
...,
[[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 13., ..., 2., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 16., ..., 16., 5., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 0., 16., ..., 15., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 15., ..., 16., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 2., ..., 6., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 2., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 14., ..., 15., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 4., 16., ..., 16., 7., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 16., 2., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 4., ..., 16., 2., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 5., ..., 12., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 10., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 2., 16., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 15., ..., 15., 0., 0.],
...,
[ 0., 4., 16., ..., 16., 6., 0.],
[ 0., 8., 16., ..., 16., 8., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 8., ..., 12., 1., 0.]]]),
'DESCR': ".. _digits_dataset:\n\nOptical recognition of handwritten digits dataset\n--------------------------------------------------\n\n**Data Set Characteristics:**\n\n :Number of Instances: 1797\n :Number of Attributes: 64\n :Attribute Information: 8x8 image of integer pixels in the range 0..16.\n :Missing Attribute Values: None\n :Creator: E. Alpaydin (alpaydin '@' boun.edu.tr)\n :Date: July; 1998\n\nThis is a copy of the test set of the UCI ML hand-written digits datasets\nhttps://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Optical+Recognition+of+Handwritten+Digits\n\nThe data set contains images of hand-written digits: 10 classes where\neach class refers to a digit.\n\nPreprocessing programs made available by NIST were used to extract\nnormalized bitmaps of handwritten digits from a preprinted form. From a\ntotal of 43 people, 30 contributed to the training set and different 13\nto the test set. 32x32 bitmaps are divided into nonoverlapping blocks of\n4x4 and the number of on pixels are counted in each block. This generates\nan input matrix of 8x8 where each element is an integer in the range\n0..16. This reduces dimensionality and gives invariance to small\ndistortions.\n\nFor info on NIST preprocessing routines, see M. D. Garris, J. L. Blue, G.\nT. Candela, D. L. Dimmick, J. Geist, P. J. Grother, S. A. Janet, and C.\nL. Wilson, NIST Form-Based Handprint Recognition System, NISTIR 5469,\n1994.\n\n.. topic:: References\n\n - C. Kaynak (1995) Methods of Combining Multiple Classifiers and Their\n Applications to Handwritten Digit Recognition, MSc Thesis, Institute of\n Graduate Studies in Science and Engineering, Bogazici University.\n - E. Alpaydin, C. Kaynak (1998) Cascading Classifiers, Kybernetika.\n - Ken Tang and Ponnuthurai N. Suganthan and Xi Yao and A. Kai Qin.\n Linear dimensionalityreduction using relevance weighted LDA. School of\n Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang Technological University.\n 2005.\n - Claudio Gentile. A New Approximate Maximal Margin Classification\n Algorithm. NIPS. 2000.\n"}
X = load_digits().data
y = load_digits().target
pics = load_digits().images
X[0].shape
(64,)
y.shape
(1797,)
pd.Series(y).value_counts()
3 183
5 182
1 182
6 181
4 181
9 180
7 179
0 178
2 177
8 174
dtype: int64
pics[7]
array([[ 0., 0., 7., 8., 13., 16., 15., 1.],
[ 0., 0., 7., 7., 4., 11., 12., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 8., 13., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 4., 8., 8., 15., 15., 6., 0.],
[ 0., 2., 11., 15., 15., 4., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 16., 5., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 9., 15., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 13., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
X[7]
array([ 0., 0., 7., 8., 13., 16., 15., 1., 0., 0., 7., 7., 4.,
11., 12., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 8., 13., 1., 0., 0., 4.,
8., 8., 15., 15., 6., 0., 0., 2., 11., 15., 15., 4., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 16., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 9., 15.,
1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 13., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
plt.imshow(pics[7],cmap='gray')
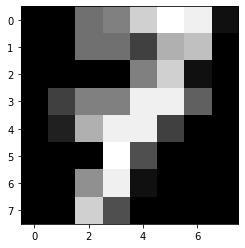
y[7]
7
划分数据集
# 划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
xtrain,xtest,ytrain,ytest = train_test_split(X,y,random_state=5)
xtrain.shape,ytrain.shape,xtest.shape,ytest.shape
((1347, 64), (1347,), (450, 64), (450,))
使用sklearn库中的KNN 模型解决问题
# 使用sklearn库中的KNN 模型解决问题
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn1 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5).fit(xtrain,ytrain)
%%time
# 预测
res = knn1.predict(xtest)
res
Wall time: 82 ms
array([5, 2, 5, 5, 5, 3, 2, 2, 3, 5, 9, 8, 7, 7, 1, 1, 5, 7, 0, 4, 5, 9,
0, 2, 1, 3, 4, 7, 5, 2, 1, 1, 2, 9, 8, 1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 5, 5, 6, 0,
1, 7, 2, 9, 7, 7, 3, 9, 5, 1, 8, 6, 7, 7, 8, 1, 6, 1, 3, 6, 1, 3,
2, 6, 8, 1, 4, 7, 1, 6, 0, 0, 5, 1, 3, 5, 1, 6, 4, 0, 4, 7, 5, 7,
8, 3, 7, 8, 5, 1, 1, 7, 5, 9, 7, 9, 3, 0, 7, 8, 7, 4, 8, 3, 2, 8,
5, 2, 7, 4, 4, 8, 9, 7, 4, 5, 0, 5, 9, 8, 2, 3, 2, 4, 4, 8, 0, 5,
2, 9, 4, 8, 6, 5, 9, 9, 8, 0, 9, 4, 3, 8, 7, 5, 5, 3, 3, 5, 1, 0,
8, 7, 2, 8, 4, 1, 0, 0, 3, 6, 4, 7, 7, 0, 4, 9, 2, 8, 7, 9, 7, 2,
0, 3, 3, 8, 5, 7, 5, 6, 8, 4, 1, 5, 1, 1, 6, 9, 9, 9, 8, 6, 4, 6,
0, 1, 6, 5, 3, 5, 0, 2, 7, 8, 8, 7, 3, 8, 3, 9, 3, 0, 9, 6, 0, 4,
0, 3, 5, 0, 4, 3, 5, 8, 8, 9, 2, 5, 0, 8, 3, 7, 4, 3, 7, 9, 2, 6,
1, 2, 1, 7, 0, 7, 5, 0, 6, 4, 1, 8, 3, 0, 8, 9, 2, 2, 5, 2, 6, 6,
3, 4, 0, 7, 1, 5, 3, 8, 7, 3, 4, 2, 5, 1, 3, 0, 0, 9, 3, 8, 8, 3,
5, 8, 6, 6, 2, 6, 7, 5, 3, 1, 5, 7, 5, 4, 5, 2, 6, 2, 0, 6, 0, 7,
2, 5, 8, 8, 7, 1, 4, 7, 2, 0, 0, 3, 7, 4, 2, 5, 2, 6, 1, 0, 5, 7,
2, 9, 1, 6, 9, 6, 5, 4, 8, 8, 0, 9, 3, 5, 7, 1, 2, 4, 1, 6, 6, 2,
1, 5, 8, 0, 3, 2, 4, 3, 9, 0, 0, 3, 2, 8, 9, 0, 2, 5, 2, 2, 5, 8,
3, 6, 7, 2, 5, 9, 0, 5, 9, 0, 1, 3, 9, 1, 4, 9, 2, 1, 5, 6, 0, 0,
9, 6, 7, 9, 9, 3, 1, 4, 3, 4, 7, 2, 5, 2, 6, 0, 3, 4, 9, 3, 1, 0,
3, 7, 6, 0, 7, 1, 0, 5, 1, 3, 5, 7, 7, 0, 1, 1, 5, 1, 1, 1, 6, 7,
7, 2, 2, 2, 7, 1, 3, 6, 9, 1])
(ytest == res).mean()
0.9822222222222222
knn1.score(xtest,ytest)
0.9822222222222222
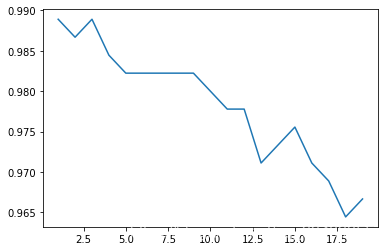
# 学习曲线
def learning_curve():
krange = range(1,20)
score = []
for i in krange:
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = i)
clf = clf.fit(xtrain,ytrain)
score.append(clf.score(xtest,ytest))
print(score.index(max(score))+1) # 打印最佳k值
plt.plot(krange,score)
plt.show()
learning_curve()
1
knn1_1 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 3).fit(xtrain,ytrain)
knn1_1.score(xtest,ytest)
0.9888888888888889
# 此时的k只是在某一特定数据集下的最优,随着测试集的变动,最优的k也会变,所以需要寻找更加稳定最优k:交叉验证法
K折交叉验证:模型稳定性
# K折交叉验证:模型稳定性
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score as CVS
def cross_validation():
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 3)
cvresult = CVS(clf,X,y,cv=10) # cv折数
c_mean = cvresult.mean()
c_std = cvresult.std()
print('cvresult:',cvresult,'cvresult.mean():',c_mean,'cvresult.std():',c_std)
# 绘制K折交叉验证曲线
score = []
var_ = []
krange = range(1,20)
for i in krange:
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = i)
cvresult = CVS(clf,xtrain,ytrain,cv = 5)
score.append(cvresult.mean())
var_.append(cvresult.var())
best_k = score.index(max(score))+1
print('best_k:',best_k)
plt.plot(krange,score,color = 'k')
plt.plot(krange,score,np.array(score)+np.array(var_)*2,c='red',linestyle = '--')
plt.plot(krange,score,np.array(score)-np.array(var_)*2,c='red',linestyle = '--')
cross_validation()
cvresult: [0.93888889 1. 0.98888889 0.97222222 0.96666667 0.97777778
0.98333333 0.98324022 0.98324022 0.97206704] cvresult.mean(): 0.9766325263811299 cvresult.std(): 0.015472517471692416
best_k: 1

归一化
# 归一化
x_train = xtrain/255
x_test = xtest/255
score=[]
var_=[]
krange = range(1,20)
for i in krange:
clf=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=i,weights = 'distance')
cvresult = CVS(clf,x_train,ytrain,cv=5)
score.append(cvresult.mean())
var_.append(cvresult.var())
plt.plot(krange,score,color='k')
plt.plot(krange,np.array(score)+np.array(var_)*2,c='red',linestyle='--')
plt.plot(krange,np.array(score)-np.array(var_)*2,c='red',linestyle='--')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x295e6cb0e50>]
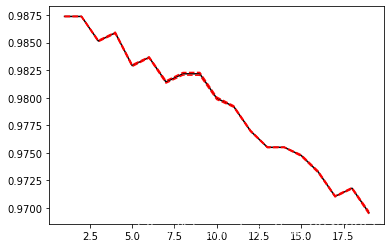
# 归一化后返回最优的k
best_index = krange[score.index(max(score))]-1
print('best_index',best_index)
print(score[best_index])
best_index 0
0.9873798705768966
使用自己写的KNN模型解决问题
# 使用自己写的KNN模型解决问题
def Knn_C(X,y,X_sample,k):
d = np.sqrt(np.sum((X-X_sample)**2,axis = 1))
knn = [*zip(d,y)]
knn.sort()
# 少数服从多数,X1的类型与最多的邻居的类型一致,取排序后的前k个值,的第二列(标签值),取第一个众数作为测试数据的预测值
Y_sample = pd.Series(np.array(knn[:k])[:,1]).mode()[0]
return Y_sample
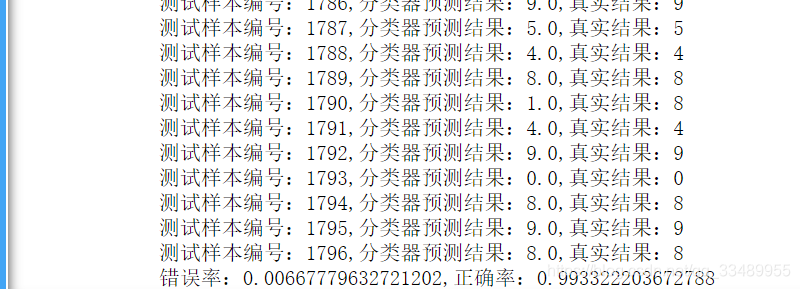
def handwtitingClassTest():
errorCount = 0.0
lenth = float(*y.shape)
for i,item in enumerate(X):
# 预测
classifierResult = Knn_C(X,y,item,3)
# 打印结果
print(f'测试样本编号:{
i},分类器预测结果:{
classifierResult},真实结果:{
y[i]}')
# 判断结果是否正确
if(classifierResult!=y[i]):
errorCount +=1.0
# print(y.shape)#(1797,)
# 打印错误率
print(f'错误率:{
errorCount/lenth},正确率:{
1-errorCount/lenth}')
handwtitingClassTest()
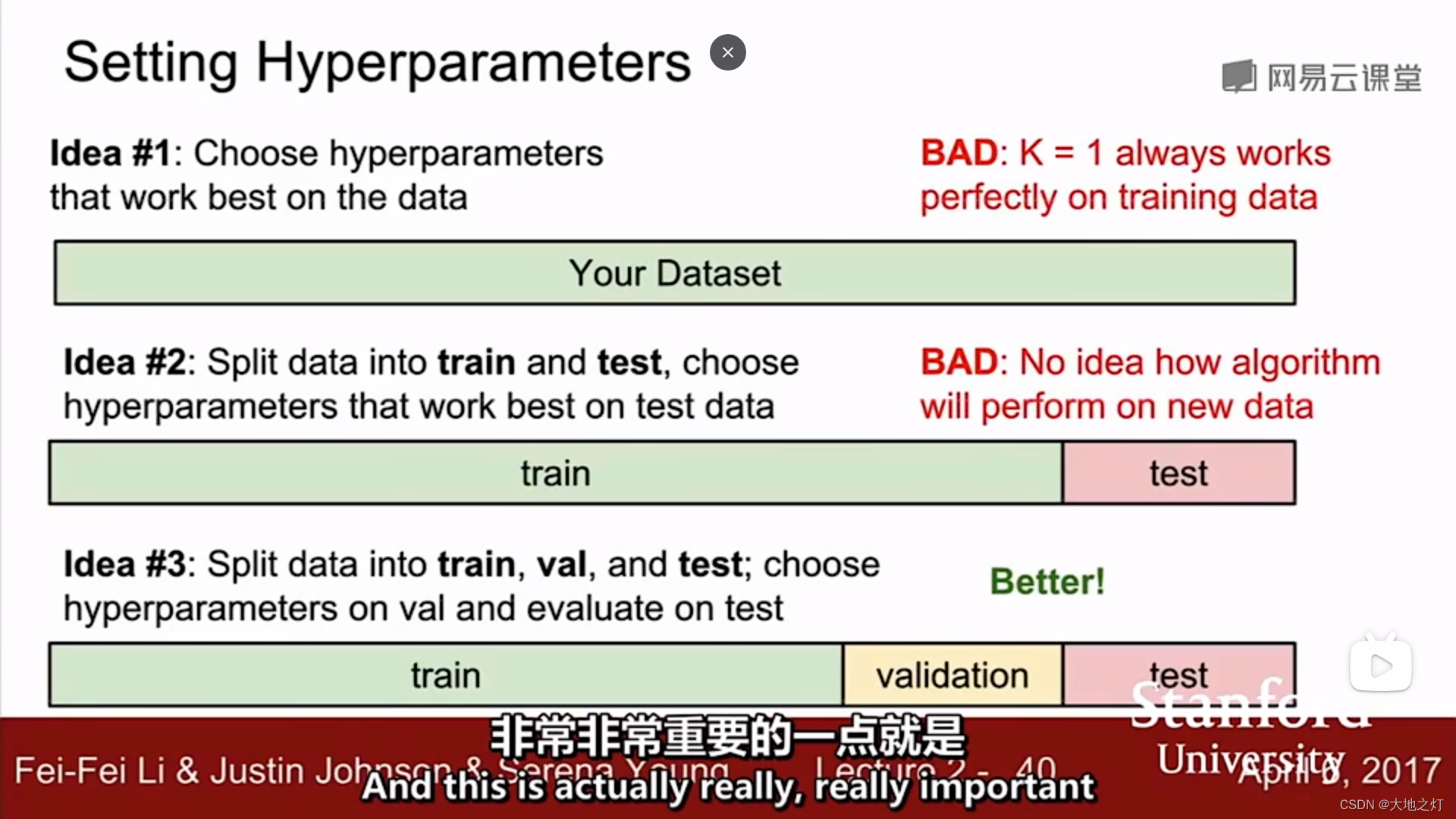
补充:(from cs231n)
视频中给出的knn代码实现

在调整超参数的时候,你不能只选择对于整个数据集有最好效果的那个参数,对于knn来说就是k=1时准确率高,但是不具备泛化性。
在调整超参数的时候,你同样不能选择在测试集上效果最好的超参数,因为这个超参数只对这个测试集有泛化性,想要得到比较准确的结果,可以进行k折交叉验证得到一个均值作为最终结果。
此外,为了避免第二种情况的发生,可以设置验证集,测试集在最终结果(确定好超参数)出来前不参与预测,保证研究的可靠性。
智能推荐
如何配置DNS服务的正反向解析_dns反向解析-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3k次,点赞3次,收藏13次。root@server ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones #添加如下内容,也可直接更改模板。[root@server ~]# vim /etc/named.conf #打开主配置文件,将如下两处地方修改为。注意:ip地址必须反向书写,这里文件名需要和反向解析数据文件名相同。新建或者拷贝一份进行修改。nslookup命令。_dns反向解析
设置PWM占空比中TIM_SetCompare1,TIM_SetCompare2,TIM_SetCompare3,TIM_SetCompare4分别对应引脚和ADC通道对应引脚-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.5w次,点赞16次,收藏103次。这个函数TIM_SetCompare1,这个函数有四个,分别是TIM_SetCompare1,TIM_SetCompare2,TIM_SetCompare3,TIM_SetCompare4。位于CH1那一行的GPIO口使用TIM_SetCompare1这个函数,位于CH2那一行的GPIO口使用TIM_SetCompare2这个函数。使用stm32f103的除了tim6和tim7没有PWM..._tim_setcompare1
多线程_进程和线程,并发与并行,线程优先级,守护线程,实现线程的四种方式,线程周期;线程同步,线程中的锁,Lock类,死锁,生产者和消费者案例-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读950次,点赞33次,收藏19次。多线程_进程和线程,并发与并行,线程优先级,守护线程,实现线程的四种方式,线程周期;线程同步,线程中的锁,Lock类,死锁,生产者和消费者案例
在 Linux 系统的用户目录下安装 ifort 和 MKL 库并配置_在linux系统的用户目录下安装ifort和mkl库并配置-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次。ifort 编译器的安装ifort 编译器可以在 intel 官网上下载。打开https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/oneapi/components/fortran-compiler.html#gs.7iqrsm点击网页中下方处的 Download, 选择 Intel Fortran Compiler Classic and Intel Fortran Compiler(Beta) 下方对应的版本。我选择的是 l_在linux系统的用户目录下安装ifort和mkl库并配置
使用ftl文件生成图片中图片展示无样式,不显示_ftl格式pdf的样式调整-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读689次,点赞7次,收藏8次。些项目时需要一个生成图片的方法,我在网上找到比较方便且适合我去设置一些样式的生成方式之一就是使用Freemarker,在对应位置上先写好一个html格式的ftl文件,在对应位置用${参数名}填写上。还记得当时为了解决图片大小设置不上,搜索了好久资料,不记得是在哪看到的需要在里面使用width与height直接设置,而我当时用style去设置,怎么都不对。找不到,自己测试链接,准备将所有含有中文的图片链接复制一份,在服务器上存储一份不带中文的文件。突然发现就算无中文,有的链接也是打不开的。_ftl格式pdf的样式调整
orin Ubuntu 20.04 配置 Realsense-ROS_opt/ros/noetic/lib/nodelet/nodelet: symbol lookup -程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.5k次,点赞6次,收藏12次。拉取librealsense。_opt/ros/noetic/lib/nodelet/nodelet: symbol lookup error: /home/admin07/reals
随便推点
操作系统精选习题——第四章_系统抖动现象的发生由什么引起的-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.4k次,点赞3次,收藏29次。一.单选题二.填空题三.判断题一.单选题静态链接是在( )进行的。A、编译某段程序时B、装入某段程序时C、紧凑时D、装入程序之前Pentium处理器(32位)最大可寻址的虚拟存储器地址空间为( )。A、由内存的容量而定B、4GC、2GD、1G分页系统中,主存分配的单位是( )。A、字节B、物理块C、作业D、段在段页式存储管理中,当执行一段程序时,至少访问()次内存。A、1B、2C、3D、4在分段管理中,( )。A、以段为单位分配,每._系统抖动现象的发生由什么引起的
UG NX 12零件工程图基础_ug-nx工程图-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.4k次。在实际的工作生产中,零件的加工制造一般都需要二维工程图来辅助设计。UG NX 的工程图主要是为了满足二维出图需要。在绘制工程图时,需要先确定所绘制图形要表达的内容,然后根据需要并按照视图的选择原则,绘制工程图的主视图、其他视图以及某些特殊视图,最后标注图形的尺寸、技术说明等信息,即可完成工程图的绘制。1.视图选择原则工程图合理的表达方案要综合运用各种表达方法,清晰完整地表达出零件的结构形状,并便于看图。确定工程图表达方案的一般步骤如下:口分析零件结构形状由于零件的结构形状以及加工位置或工作位置的不._ug-nx工程图
智能制造数字化工厂智慧供应链大数据解决方案(PPT)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读920次,点赞29次,收藏18次。原文《智能制造数字化工厂智慧供应链大数据解决方案》PPT格式主要从智能制造数字化工厂智慧供应链大数据解决方案框架图、销量预测+S&OP大数据解决方案、计划统筹大数据解决方案、订单履约大数据解决方案、库存周转大数据解决方案、采购及供应商管理大数据模块、智慧工厂大数据解决方案、设备管理大数据解决方案、质量管理大数据解决方案、仓储物流与网络优化大数据解决方案、供应链决策分析大数据解决方案进行建设。适用于售前项目汇报、项目规划、领导汇报。
网络编程socket accept函数的理解_当在函数 'main' 中调用 'open_socket_accept'时.line: 8. con-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2w次,点赞38次,收藏102次。在服务器端,socket()返回的套接字用于监听(listen)和接受(accept)客户端的连接请求。这个套接字不能用于与客户端之间发送和接收数据。 accept()接受一个客户端的连接请求,并返回一个新的套接字。所谓“新的”就是说这个套接字与socket()返回的用于监听和接受客户端的连接请求的套接字不是同一个套接字。与本次接受的客户端的通信是通过在这个新的套接字上发送和接收数_当在函数 'main' 中调用 'open_socket_accept'时.line: 8. connection request fa
C#对象销毁_c# 销毁对象及其所有引用-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.3k次。对象销毁对象销毁的标准语法Close和Stop何时销毁对象销毁对象时清除字段对象销毁的标准语法Framework在销毁对象的逻辑方面遵循一套规则,这些规则并不限用于.NET Framework或C#语言;这些规则的目的是定义一套便于使用的协议。这些协议如下:一旦销毁,对象不可恢复。对象不能被再次激活,调用对象的方法或者属性抛出ObjectDisposedException异常重复地调用对象的Disposal方法会导致错误如果一个可销毁对象x 包含或包装或处理另外一个可销毁对象y,那么x的Disp_c# 销毁对象及其所有引用
笔记-中项/高项学习期间的错题笔记1_大型设备可靠性测试可否拆解为几个部分进行测试-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1w次。这是记录,在中项、高项过程中的错题笔记;https://www.zenwu.site/post/2b6d.html1. 信息系统的规划工具在制订计划时,可以利用PERT图和甘特图;访谈时,可以应用各种调查表和调查提纲;在确定各部门、各层管理人员的需求,梳理流程时,可以采用会谈和正式会议的方法。为把企业组织结构与企业过程联系起来,说明每个过程与组织的联系,指出过程决策人,可以采用建立过程/组织(Process/Organization,P/O)矩阵的方法。例如,一个简单的P/O矩阵示例,其中._大型设备可靠性测试可否拆解为几个部分进行测试